A research team from the University of Warsaw, Mossakowski Medical Research Institute, National Medicines Institute and Warsaw University of Life Sciences reported studies on a new organic compound with potential applications in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. The results were published in Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics.
Researchers from the University of Warsaw, together with scientists from Mossakowski Medical Research Institute, National Medicines Institute and Warsaw University of Life Sciences, conducted investigations on a new organic compound with potential applications in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Both the compound, and its conjugate with gold nanoparticles, reveal considerable inhibitory properties against acetylcholinesterase, the enzyme responsible for the hydrolysis of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter whose deficit is observed in patients with Alzheimer’s disease.
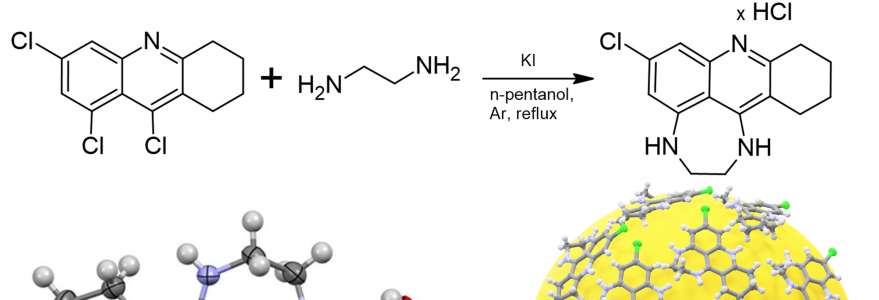
The compound was synthesized by Dr Anna Zawadzka from the UW Faculty of Chemistry and then subjected to comprehensive characterization, starting from the crystallographic structure, through electrochemical and optical properties, to biological activity.
“We conducted the studies in an interdisciplinary team. Experts from various fields were involved, from organic synthesis and nanotechnology to in vitro and in vivo investigations on animals,” said Prof. Maciej Mazur from the Department of Chemistry, University of Warsaw.
Both the compound, which is a derivative of tetrahydroacridine, and its conjugate with gold nanoparticles, exhibit the ability to inhibit acetylcholinesterase about 5,000 times more effectively than rivastigmine, a drug commonly used in the therapy of Alzheimer’s disease. Therefore, it may be significantly more effective while being less toxic.
Alzheimer’s disease is a neurodegenerative disorder that represents an increasing burden on health, society, and economy. It is the most common cause of dementia, characterized by cognitive dysfunctions such as memory impairment, thinking problems, and learning disabilities.
The article was published in Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics.
The work was carried out by research teams from the Faculty of Chemistry, University of Warsaw (Ilona Mojzych, Anna Zawadzka, Maciej Chotkowski, Maciej Mazur), Mossakowski Medical Research Institute (Katarzyna Kaczyńska, Dominika Zając, Piotr Wojciechowski), National Medicines Institute (Jan K. Maurin), and Warsaw University of Life Sciences (Katarzyna Wiktorska).